In late 2022, Ticketmaster experienced a massive number of system requests – 3.5 billion – when online ticket sales opened for Taylor Swift’s Eras Tour. It was determined the excessive traffic was largely driven by bots. This resulted in the cancellation of ticket sales for the pop icon’s Eras Tour. The headlines focused on this topic for weeks, which may have you wondering, “Are bots dangerous or a threat to my business?”
While you may often hear about the chaos caused by bots, are you aware of what they are and how they can be used in a business like yours? Bots are used across most industry sectors. Let’s review seven things you should know about bots and how they may impact your business, including from a cybersecurity threat perspective.
1. What are Bots and are They All Bad?
As you might anticipate, the term “bot” is short for “robot.” Bots are a type of software program designed to perform repetitive tasks, such as requesting thousands of concert tickets before fans can make their purchase. They imitate the online behaviors of real people but work much faster than someone typing on a keyboard or tapping on a phone screen. By that same token, bots were initially created to carry out useful tasks. These are examples of so-called good and bad bot activity.
- Chatbots: The friendly voice of Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri are examples of helpful bots. These virtual assistants help users make music selections, identify GPS coordinates, and even negotiate smart technologies such as lights and thermostats. Chatbots have been around since 1966 when the Massachusetts Institute of Technology created a virtual psychotherapist that answered questions with questions. A clever and witty beginning, to say the least.
- Spiders or Crawlers: Major search engines such as Google and Bing use web-crawling bots to access websites and gather information. When internet users run searches, the bots are partially responsible for compiling the list that comes up.
- Spambots: These bad bots are designed to steal email addresses from contact lists. They also post content on platforms that entices people to click through to certain websites.
- Malicious Chatterbots: Dating services and social media platforms are rife with bots. They mimic human beings, often to trick people into divulging personal and financial information such as credit card numbers.
Perhaps the most dangerous type of bot attack on your business involves those laced with malicious software. Many hide in a network and perform tasks that mirror legitimate users. The longer they remain undetected, the more sensitive and valuable digital assets can be scraped.
2. How Can Bots Impact My Business?
With the rise of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, bots are evolving to handle an increased number of tasks. If companies relied upon employees to manage now-automated digital interactions, the cost of doing business would likely be prohibitive.
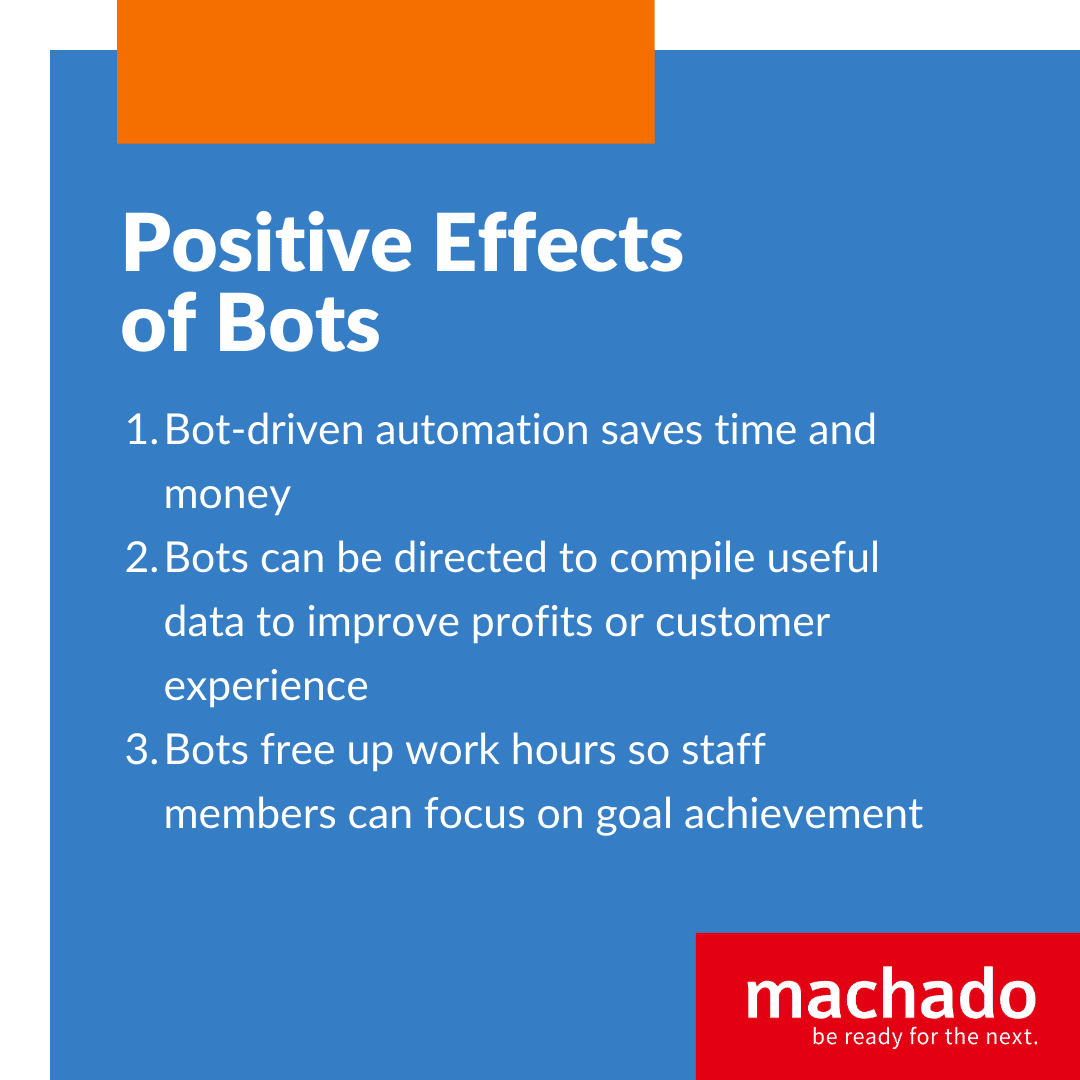
Bots are commonly used in customer service and for boosting productivity. When you visit an organization’s website, that helpful chat feature that pops up with the image of a youthful human is most likely a bot that helps customers to fulfill their needs. These are other ways bots can have a positive effect on your businesses.
- Bot-driven automation saves time and money.
- Bots can be directed to compile useful data to improve profits or customer experience.
- Bots free up work hours so staff members can focus on goal achievement.
The vast majority of industry leaders build a cybersecurity posture to prevent well-known schemes and threats. These usually involve brute force attacks, distributed denial of service (DDoS), ransomware, and phishing schemes. Companies determined to deter hackers often invest in cybersecurity awareness training that teaches employees what to expect from hackers. By contrast, few are prepared for a bot attack.
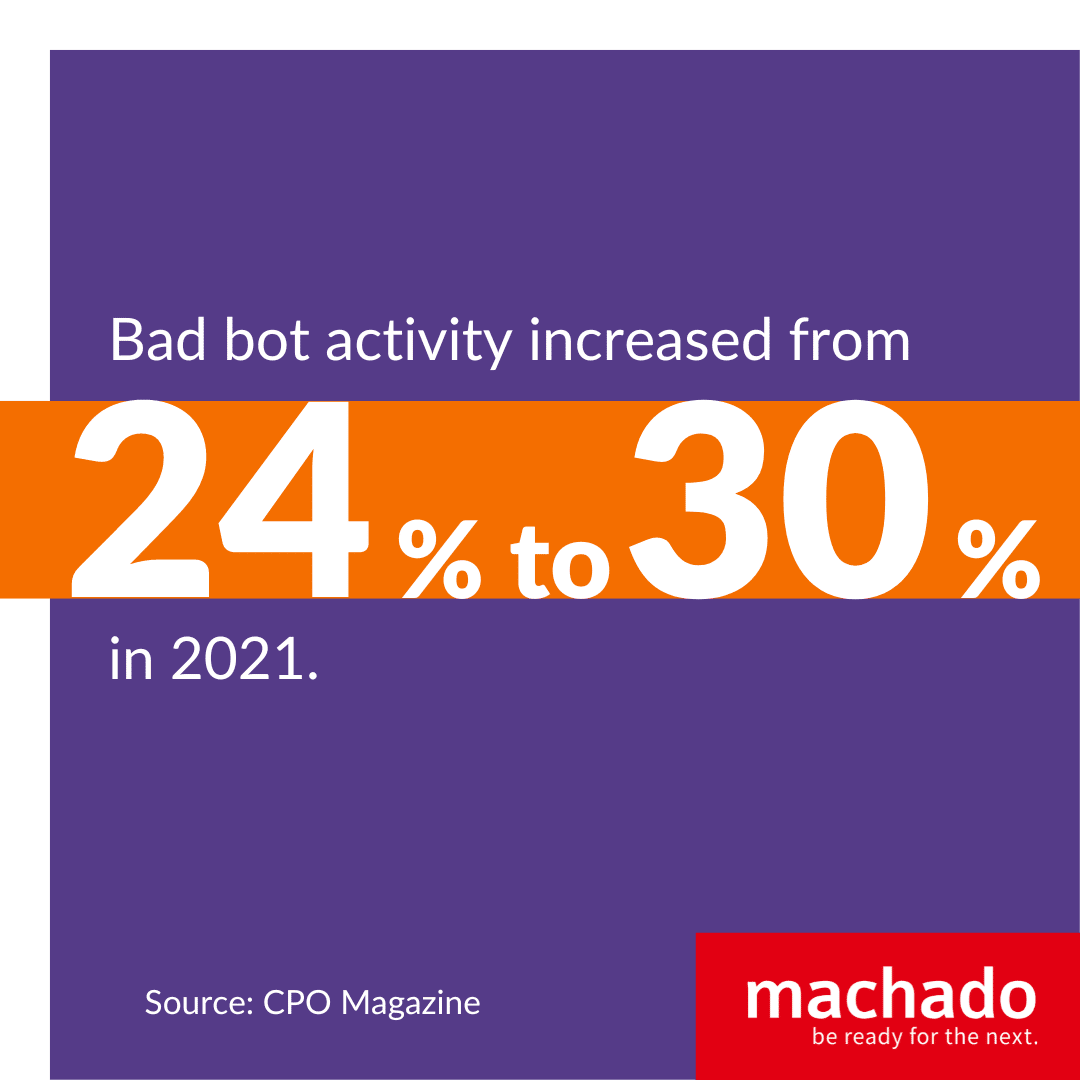
Bot attacks rank among the growing cybersecurity threats. Non-human activity comprised 42.3 percent of all internet activity during 2021, and bad bot activity increased from 24 to 30 percent by year’s end, according to CPO Magazine. That’s a staggering amount of nefarious activity and hackers are expected to double down in 2023. These are ways cybercriminals may use a bot attack to harm your organization:
- Swell online carts with products, thereby reducing sellable inventories.
- Target user profiles by employing stolen login credentials.
- Scrape a business platform to gather intel and create fake loan and credit card applications.
- Use scraped information to build a look-a-like website to scam a business’s customers.
It’s important to understand that a bot attack doesn’t just result in quantifiable business losses. One of the most debilitating and lingering effects involves reputational harm. Customers and companies in your orbit will likely shy away from doing business in the future because of a hack. Upwards of 60 percent of small and mid-sized businesses close within six months following a cyberattack.
Those charged with making cybersecurity investments would also be well-served to know that hackers can take over entire networks. They can also use your system as a bot network command center to launch attacks.
3. What is a Botnet and Botnet Attack?
When cybersecurity professionals talk about a “botnet” or “botnet attack,” they are referring to the end result of a cybersecurity breach. A single bot infiltrates a company device or desktop and lays in wait.
It may conduct tasks that mimic those of staff members as it hides in plain sight. Once a single bot thoroughly infects a device or desktop, it can spread to other vulnerable computers. Eventually, the bot can create a network of infected computers and mobile devices. At this juncture, it has evolved into a botnet and possesses superior attack power.
The organization’s devices that fall under the control of the cybercriminal behind the botnet are typically called “zombies.” And the hacker responsible is usually deemed the “bot herder.” Like an episode of The Walking Dead, your entire business network can be used like a hoard to attack unsuspecting organizations and carry out criminal activity. These are reasons why companies and their leadership teams suffer a sullied reputation following a botnet attack.
4. Are There Different Types of Botnet Attacks?
It may be difficult to imagine that someone has taken control of and effectively weaponized your operation’s electronic devices. But the hard truth about running an honest enterprise is that hackers level an attack about every 39 seconds. And one in three Americans are impacted every day.
Each time cybersecurity professionals develop a way to protect companies from cyberattacks, digital thieves devise new methods of dishonesty. These are ways botnet attacks are being deployed.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed denial of service attacks are orchestrated by zombies sending out massive amounts of requests and information. This type of botnet attack overwhelms a platform, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Spam Attacks: Botnets are responsible for the vast majority of spam attacks. Emails and comment section messages are laced with malware designed to ensnare unsuspecting people. This type of botnet attack is capable of launching millions of spam messages every day.
- Data Breaches: Hackers can make a pretty penny selling your confidential information on the dark web. That’s why online criminals use botnet attacks to steal data linked to credit cards, bank accounts, social security numbers, and e-commerce data, among others. This type of botnet attack represents yet another criminal evolution from brute force methods.
- Monitoring: When bots go undetected, the botnet may gain the ability to monitor the activity of staff members. Discovering usernames and passwords allows hackers to circle back and pilfer off valuable digital assets with impunity.
It’s also not unusual for cybercriminals to empower botnets to expand their reach by spreading to other networks. Vulnerable personal devices with access to the business network are like low-hanging fruit to hackers. When the botnet spreads to other operations in your industry, a loss of reputation may be imminent.
5. How Would I Know if My Infrastructure was Attacked by Bots?
Bot attacks present a significant detection challenge. They have the bandwidth to simultaneously orchestrate attacks across endpoints and apps as well as websites. Because bot activity can look exactly like that of human users, distribute the footprint, and rotate criminal intent through an untold number of otherwise clean IPs. Although identifying the telltale signs of a bot attack proves challenging, hackers may leave breadcrumbs.
- Excessive Traffic: If the amount of incoming and outgoing traffic on your platform shows abnormal spikes, you may be the victim of a botnet DDoS attack.
- Excessive Memory Usage: A botnet tends to use significant amounts of the system’s resources. If memory usage spikes, you may be part of a botnet.
- Outgoing Traffic: If a large portion of your outgoing traffic is focused toward a single or limited number of destinations, that’s a sign. If you do not recognize those points, it’s likely someone has operational control over your network.
It’s true that bots and botnet attacks are sophisticated hacking schemes designed to evade detection. That does not mean cybersecurity professionals are willing to concede to criminals. There are tried-and-true cybersecurity measures any business can take to deter and repel these threats.
6. How Can I Prevent a Bot Attack on My Business?
Bot attacks may seem so futuristic that people outside the managed IT and cybersecurity fields believe they cannot be stopped. Nothing could be further from the truth. Many of the same cyber hygiene practices employed to deter garden variety hackers are equally effective against determined adversaries. These familiar cybersecurity practices can harden your defenses and prevent a bot attack.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Having an educational component in place provides staff members with the knowledge they require to prevent an attack. When your frontline workers can identify phishing emails and understand not to click on malicious applications, hackers cannot get their bot into the network.
- Software Updates: Cybercriminals leverage outdated and unpatched software products to gain entrance to business networks. Prioritizing software updates ensures this gap has been closed.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Requiring legitimate network users to enter a secondary code ranks among the best defenses against unauthorized access. Employees enter their username, password, and wait a few seconds to receive an authentication code on another device. Unless a hacker has stolen someone’s secondary device, they cannot know the code.
Cybercriminals are well aware that staff members generally access business networks from personal devices. That’s why endpoint devices must undergo the same level of cybersecurity protection as office desktops.
7. What Can I Do if My Business is Impacted by Bots?
Are bots dangerous to your business? That depends on whether they are being used to improve efficiency, productivity, and reduce costs. If bad bots have somehow infiltrated your system, it’s critical to contact a cybersecurity expert to help you take proactive measures to expel them. The longer a bot attack persists, the greater the chance of hackers turning your business into an aggressive botnet and damaging your reputation. Let’s talk about what you can do today to protect your business from unwanted bots tomorrow..
Be Ready for the Next Cyberattack
Download our free guide on staying protected from ransomware.
Be Ready for the Next Cyberattack
Download our free guide on staying protected from ransomware.