Cybersecurity threats persist year after year because hackers come up with new schemes to steal valuable and sensitive information from you and your business. Several of the 2023 cybersecurity trends have evolved from previous years. That’s largely due to hackers adapting to cybersecurity defenses developed through 2022. Recent data confirms that whether you’re responsible for managing a small, mid-sized, or large company, hackers are continuing to target you with impunity. Here are a few statistics that should catch your attention:
- Upwards of 14.78 million data breaches occurred during the third quarter of 2022 alone.
- Data breaches during the third quarter increased by 167 percent compared to the previous quarter.
- The average cost of a data breach rose to $4.35 million in 2022.
- The healthcare industry sustained the highest average loss.
While you — as well as the general public — are keenly aware of pervasive cybersecurity threats, only approximately half of small businesses have a cybersecurity plan in place. A hacker sitting in a café halfway around the world also knows American employees lack cybersecurity awareness training and are easily preyed upon. If you’re among the many industry leaders concerned about emerging threats, consider the following 2023 cybersecurity trends and plan now to update your defenses for the new year.
1. Geo-Targeted Phishing Threats
Reports indicate that hackers leveled more than 255 million phishing attacks during the first half of 2022. That figure marks a 61 percent increase over 2021. It also reinforces the fact that garden variety hackers rely heavily on electronic messaging in hopes an employee makes a critical mistake. As an increased number of security-savvy business leaders provide cybersecurity awareness training for employees, online thieves have honed their attacks.
Geo-targeted phishing involves cybercriminals narrowing down their scheme to certain people. Using terminology typically used by industry insiders and words that imply the sender is local, frontline workers are more easily convinced a message is authentic. This technique is generally deployed by more determined and sophisticated cybercriminals. It eliminates the common word choice and grammatical errors people who undergo basic cybersecurity awareness training identify. The use of geo-targeted phishing schemes is expected to become highly personalized and localized. It’s essential for business leaders to up the cybersecurity awareness training ante to account for geo-targeted phishing ploys.
Be Ready for the Next Cyberattack
Download our free guide on staying protected from ransomware.
2. Increased Threats to the Healthcare Industry
Healthcare sector businesses are expected to remain high-value targets for hackers. Being included in the 2023 cybersecurity trends may not necessarily come as a surprise. The ability of cybercriminals to turn a profit on Personal Identifying Information (PII) and Protected Health Information (PHI) on the dark web makes healthcare a veritable treasure trove for digital thieves.
“From 2015 to 2019, 157.40 million records were exposed, that is, 63.19 percent of the total. In addition, out of 249.09 million records, 161.05 were exposed through hacking attacks that comprised 64.65 percent of the total exposed health records from 2005 to 2019,” according to the National Institute of Health. “Thus, it is evident that the healthcare industry has been inundated by hackers in the last five years, compromising 90.49 percent of health records during this time period.”
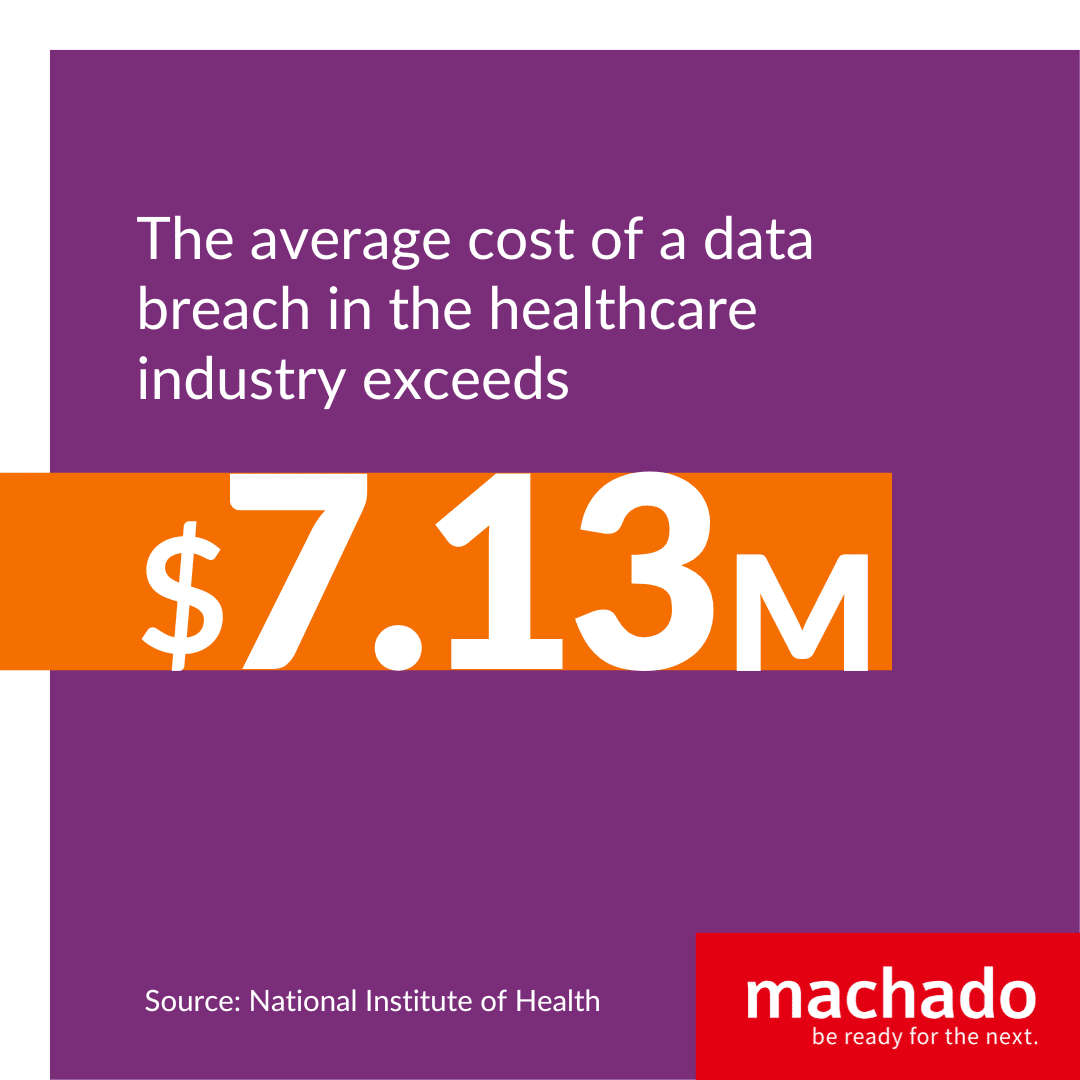
The average cost of a data breach in the healthcare industry exceeds $7.13 million. Given the rise of telemedicine and remote healthcare connectivity, hackers are expected to target PHI and PII at a potentially unprecedented level in 2023.
3. Targeted Threats to Higher Education
Cyberattacks in the education sector have risen substantially in recent years. When students pivoted to online learning during the height of the pandemic, hacking attacks on platforms such as Zoom made splashy headlines. Privacy descended to the point where the Chicago Tribune ran a headline that included the term “Zoombombing.” These and other factors have made higher education a preferred target of nefarious hacking groups.
Cyberattacks on education institutions in 2022 grew by approximately 44 percent compared to 2021. Higher education decision-makers would be well-served to onboard managed IT and cybersecurity experts to revisit their defensive posture. The growing use of personal devices and remote off-campus learning provides hackers with exploitable gaps.
The need for post-perimeter security and endpoint protection has never been greater. That’s because hackers routinely target electronic devices such as smartphones, iPads, and personal computers to gain access to higher education networks. Once inside, PII and even PHI records can be stolen and sold on the dark web.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to Play Greater Role
One of the positive 2023 cybersecurity trends involves the creative use of AI and ML in combating cybersecurity threats. The advanced technologies being developed are expected to make deterring online thieves simpler and more efficient.
Through the use of ML, patterns are identified and algorithms can be developed to anticipate cyberattacks. The advanced warning allows an organization’s defensive protocols to respond in real-time. The AI side of the equation highlights data that appears vulnerable or exploitable, giving cybersecurity teams the ability to take proactive measures.
Integrating AI and ML changes the cybersecurity battlefield significantly heading into 2023. Rather than deploy disaster restoration strategies, security teams can confront threat actors before they even breach the castle walls.
5. IoT with 5G Network
Although new technologies support business productivity and goal achievement, Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rollout of 5G networks increase the risk of cybersecurity gaps. For example, a 2019 Symantec report indicates that compromised routers accounted for 75 percent of IoT-based cyberattacks in 2018. Even items such as digital cameras posed a 15 percent risk.
“It’s been more than two years since, in the fall of 2016, the threat of cyber attacks that leveraged Internet of Things (IoT) devices moved from theoretical to actual. That fall, several distributed denial of service (DDoS) assaults each leveraged tens of thousands of poorly secured IoT devices to send crippling volumes of traffic to targeted web sites,” according to a Symantec blog post.
As my “Cybersecurity in Healthcare: 6 Ways To Protect Your Business and Patients” article points out, the market for IoT devices was expected to balloon to 14.4 billion connections in 2022 and hit 27 billion in 2025. Healthcare sector organizations can expect increased vulnerabilities as device manufacturers are not necessarily keeping pace with emerging cybersecurity threats.
6. Predictive Cloud Security
Have you, like the vast majority of organizations, transitioned from in-house networks to the Cloud? More than 90 percent of businesses pivoted to the Cloud after the pandemic disrupted the ability to work from brick-and-mortar facilities.
Accessing data and performing tasks remotely has provided wide-reaching benefits to your business. These include reduced office space needs and the ability to hire talented people outside traditional commuter radiuses. Unfortunately, hackers have also been following the trend, and they continue to plot ways to take advantage of Cloud users.
One of the 2023 cybersecurity trends — from a defensive lens — involves placing a heightened focus on data storage and transmission. Because not all Cloud services automatically provide secure encryption, authentication, and audit logging, managed IT cybersecurity firms are filling such needs. Along with hardening defenses to prevent hackers from exploiting login credentials and data movement, predictive security is blossoming.
Predictive security has emerged as a proactive measure that helps identify cybersecurity threats before hackers pounce. Emerging threats can be discovered trying to pass through IoT devices to bypass endpoint security measures. Applying predictive security to Cloud-based operations gives security professionals the advanced warning necessary to respond and deter an attack.
Although honest business professionals are gaining leverage over Cloud-based cyberattacks, another tried-and-true measure finds its way into the 2023 cybersecurity trends — multi-factor authentication. Requiring network users to receive a code from a secondary device before accessing a business network ranks among the foundational defenses. It continues to trend into 2023 for good reason.
7. More Focus on Compliance Regulations
Meeting government mandates ranks among the most impactful 2023 cybersecurity trends as you are tasked with new compliance regulations. An increased number of companies participating in international commerce could be saddled with multiple sets of cybersecurity requirements.
The U.S. Department of Defense plans to publish interim rules for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) as early as March and contractors can anticipate seeing compliance language in agreements by July 2023. The CMMC rollout is expected to include upwards of 300,000 organizations that do business within the military-industrial base.

Compliance may also involve meeting cybersecurity standards established in the EU. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for example, is designed to protect data and privacy overseas. When U.S. companies bring goods and services to European consumers, the GDPR is likely to be triggered. That means outfits turning profits from transactions with EU residents will need to maintain compliance with U.S. and EU cybersecurity regulations.
8: More Focus on Cybersecurity Awareness
Cybersecurity awareness training will, again, be a primary focus among 2023 cybersecurity trends. Employees continue to be targeted by hackers knowing a high number of network users have not been adequately educated. Verizon’s 2022 Data Breaches Investigations Report supports this year-over-year conclusion. It indicates that 82 percent of data breaches result from human error.
Valued and loyal staff members sometimes disclose critical personal information on professional platforms such as LinkedIn or common social media profiles. Names, dates of birth, addresses, and information about loved ones can be used for social engineering schemes or to guess passwords.
Anyone who has access to an organization’s network and digital assets remains vulnerable without thorough and ongoing cybersecurity awareness training. Your 2023 employee training plans should include web-based and in-person cybersecurity instruction. Key focus areas include identifying phishing emails, recognizing attempts to give their login credentials, and knowing to never click on unknown links or download unvetted files. Proactive business leaders, like you, are more inclined to work with cybersecurity experts who can provide preemptive alerts regarding emerging threats.
Although the vast majority of data breaches are caused by honest mistakes, companies are expected to take a trust-but-verify approach to new hires to prevent inside jobs.
How is Your 2023 Cybersecurity Readiness?
Several of the 2023 cybersecurity trends evolved from years of hackers devising new schemes to steal from you and your hard-working team. While you may have already educated your staff about phishing schemes, now you’re confronted with geo-targeted phishing attacks. And threats from rogue nations will be met with updated CMMC compliance mandates.
Be Ready for the Next Cyberattack
Download our free guide on staying protected from ransomware.
It seems each year business leaders need to invest in cybersecurity threat deterrence on new fronts. Let’s discuss what you can do today to be confident with your cybersecurity preparedness.